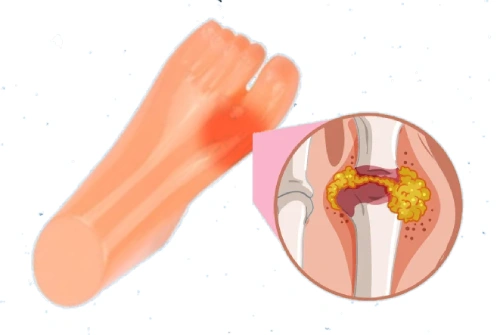
Over time, recognizing the signs of gout can significantly improve your quality of life. As a painful form of arthritis characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, gout is often associated with the formation of uric acid crystals in your joints. In this blog post, you will learn six crucial steps to effectively identify these crystals, helping you understand your condition better and enabling you to take proactive measures for management and relief.
The Biochemistry of Uric Acid Crystals
The formation of uric acid crystals within your joints is a result of metabolic processes that involve purines, which are naturally occurring substances in certain foods and your body’s cells. When your body breaks down purines, it produces uric acid as a byproduct. Typically, uric acid is dissolved in the blood and eliminated through the kidneys. However, when levels reach excessive amounts, uric acid can crystallize, leading to inflammation and pain characteristic of gout.
How Uric Acid Forms in the Body
Uric acid forms as your body metabolizes purines, component compounds found in certain foods such as organ meats, seafood, and some vegetables. Under normal conditions, your kidneys filter and excrete uric acid. Yet, when a surge in purine consumption occurs or your kidneys fall short in excretion, the uric acid levels in your bloodstream spike, leading to potential crystal formation in the joints.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle Factors
Your dietary choices and lifestyle habits heavily influence uric acid levels in your body. High-purine foods can cause elevated levels of uric acid, while hydration plays a vital role in flushing it out. Risk factors like alcohol consumption and obesity further contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Incorporating healthier food options and regular exercise can help mitigate these risks.
- Avoid high-purine foods such as red meat, shellfish, and sugary beverages.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limit alcohol intake, particularly beer and spirits, which can elevate uric acid levels.
- Maintain a healthy weight to lower your overall risk of gout attacks.
- Perceiving these dietary dynamics plays a significant role in managing your risk.
Making intentional dietary and lifestyle adjustments fosters better management of uric acid levels in your body. Foods rich in vitamin C, low-fat dairy, and whole grains can help reduce the incidence of gout attacks. Emphasis on hydration, combined with regular physical activity, serves to promote better kidney function and uric acid excretion. Perceiving these aspects of your lifestyle ensures a proactive approach to preventing and managing gout effectively.
- Focus on incorporating fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants.
- Consider maintaining healthy body weight through a balanced diet.
- Pay attention to your portion sizes, particularly with high-purine foods.
- Engage in regular physical activity to aid in metabolism and overall health.
- Perceiving these changes can lead to significant improvements in your gout management journey.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gout
Being familiar with the symptoms of gout plays a vital role in timely recognition and management. Typically, acute gout flares lead to intense pain and inflammation, often awakening you from sleep. Your body responds with visible symptoms, allowing you to identify the need for medical attention.
Distinctive Pain and Discomfort Signals
Gout manifests as sharp, excruciating pain, often focused around the big toe. This pain can strike suddenly, often peaking within 24 hours. You may also experience a relentless throbbing sensation that may discourage movement or contact with the affected joint, making daily activities seem daunting.
Identifying Swelling and Inflammation Patterns
Alongside intense pain, swelling and inflammation are clear indicators of an impending gout attack. You’ll notice the affected joint becoming reddened and swollen, often appearing warm to the touch. This inflammation can also extend to the surrounding areas, making it increasingly uncomfortable and difficult to manage.
In a gout flare, swelling may not only affect the big toe but can also involve other joints, such as the ankles, knees, and wrists. You might find that the skin over the swollen joint stretches tight, resulting in a shiny appearance. Tracking these patterns can be helpful, as persistent inflammation could indicate the need for adjustments in your dietary or medicinal management strategies. Engaging with a healthcare professional once these symptoms arise is vital to prevent further complications, such as joint damage or chronic gout.
Diagnostic Techniques for Gout
Diagnosing gout involves a blend of clinical evaluation and specialized testing. Initially, your healthcare provider will assess your medical history and perform a physical examination to identify symptoms like swelling and redness in joints. Following this assessment, specific diagnostic techniques are employed to confirm the presence of uric acid crystals and guide treatment options effectively.
Laboratory Tests to Detect Uric Acid Levels
Your doctor may order a serum uric acid test, which measures the amount of uric acid in your blood. Elevated levels often indicate a higher risk of gout, though not everyone with high uric acid will develop the condition. Joint fluid analysis is another key lab test; it involves extracting fluid from an inflamed joint to check for the presence of monosodium urate crystals under a microscope, providing a definitive diagnosis.
Imaging Methods: When and Why They Matter
Imaging techniques such as X-rays, ultrasounds, and CT scans can be valuable tools in diagnosing gout. These methods help visualize joint abnormalities and provide evidence of crystal deposits, though they are not always the first choice in identifying an active gout attack. Instead, imaging is often utilized to assess joint damage over time or differentiate gout from similar conditions.
Ultrasound, in particular, has gained traction in gout diagnosis due to its ability to detect tophi, which are round deposits of uric acid crystals that accumulate in soft tissues. This method is non-invasive and does not involve radiation, making it suitable for assessing chronic cases. In some instances, CT scans reveal even subtle deposits of these crystals, further confirming a gout diagnosis and helping tailor your treatment plan effectively. Understanding these imaging methods and their applications allows you to better navigate the diagnostic journey and be proactive in managing your condition.
Effective Strategies for Managing Gout Symptoms
Managing gout symptoms effectively involves a multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Simple adjustments can often lead to significant relief, while medications can help control pain and prevent future flare-ups. Adopting strategies tailored to your unique situation can pave the way for better management of this painful condition.
Lifestyle Adjustments That Make a Difference
Making specific lifestyle changes can substantially impact your gout management. You’ll want to focus on maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and adopting a balanced diet low in purines. Incorporating regular exercise can also enhance joint function and reduce the risk of flare-ups. Small changes, like substituting sodas with water and reducing alcohol intake, can make a notable difference in your uric acid levels.
Medication Options: How They Work and Their Efficacy
A variety of medications are available to help manage gout symptoms and lower uric acid levels. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen provide immediate pain relief during flare-ups. Colchicine works by reducing inflammation and can help prevent future attacks. For long-term management, uric acid-lowering medications such as allopurinol effectively reduce uric acid production, thus lowering the likelihood of gout attacks. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best options for your condition.
Understanding how these medications operate is vital for effective gout management. NSAIDs alleviate pain and inflammation during acute flare-ups, while colchicine targets the inflammatory response directly at the joint level, providing relief from swelling and discomfort. Uric acid-lowering medications, like allopurinol and febuxostat, work by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for uric acid production, helping to maintain lower uric acid levels over time. You may also encounter corticosteroids, particularly in cases where other medications are ineffective, providing rapid relief. Always engage with your healthcare team to tailor a medication strategy that aligns with your symptoms and lifestyle needs.
The Larger Picture: Long-term Health Implications of Gout
Chronic gout can lead to serious long-term health issues, including joint damage and other systemic complications. As uric acid levels rise and fall, they can cause inflammation that not only affects your joints but also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, kidney problems, and diabetes. The ongoing presence of uric acid crystals may create a cycle of pain, leading to decreased mobility and a reduced quality of life. Addressing gout early on is vital in mitigating these risks and preserving your overall health.
The Relationship Between Gout and Other Health Issues
Your risk of other health conditions increases significantly with untreated or chronic gout. Studies show that individuals with gout are 50% more likely to suffer from heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. The inflammation resulting from gout may contribute to the development of these health issues, highlighting the interconnectedness of chronic conditions. Being aware of these potential complications can motivate you to adopt preventive measures early.
Understanding Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Certain lifestyle factors place you at heightened risk for developing gout, including obesity, a high-purine diet, and excessive alcohol consumption. To prevent gout flare-ups, focus on maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and limiting purine-rich foods such as red meat and seafood. Regular exercise and routine health check-ups can also help manage uric acid levels effectively. Recognizing these risk factors empowers you to take control of your health.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Limit purine-rich foods in your diet.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Stay consistent with health check-ups.
Addressing the risk factors associated with gout requires dedication to lifestyle modifications and proactive health management. This includes dietary changes such as reducing the intake of red meats and organ meats, which are high in purines, and managing alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits. Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy into your diet can further aid in lowering uric acid levels. Staying consistent with these practices not only manages gout symptoms but can also enhance your overall well-being. Recognizing these strategies is the first step toward long-term health.
- Commit to a low-purine diet.
- Incorporate more whole grains and vegetables.
- Limit intake of sugary drinks.
- Monitor your body weight regularly.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Steps To Fully Understand Gout Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of gout—like uric acid crystal buildup, joint pain, and dietary triggers—is an important first step toward managing your condition. But don’t go it alone. By speaking with a custom orthotics professional in Edmonton, like the team at Custom Orthopedic, you can take a more proactive approach to relieving foot pain and preventing future flare-ups. Whether it’s through personalized footwear, pressure relief, or expert guidance, we’re here to help you move comfortably and confidently every step of the way.